 |
 |
Post Archive
January (2)
Have we entered the era of the 1 year sequencer release cycle? *Updated*
Tuesday, January 13, 2015
Illumina's $1000 Genome*
Wednesday, January 15, 2014
2013 (4)Have we entered the era of the 1 year sequencer release cycle? *Updated*
Tuesday, January 13, 2015
Illumina's $1000 Genome*
Wednesday, January 15, 2014
May (1)February (3)
A coming of age for PacBio and long read sequencing? #AGBT13
Saturday, February 23, 2013
Next Generation Sequencing rapidly moves from the bench to the bedside #AGBT13
Friday, February 22, 2013
#AGBT day one talks and observations: WES/WGS, kissing snails, Poo bacteria sequencing
Wednesday, February 20, 2013
2012 (5)A coming of age for PacBio and long read sequencing? #AGBT13
Saturday, February 23, 2013
Next Generation Sequencing rapidly moves from the bench to the bedside #AGBT13
Friday, February 22, 2013
#AGBT day one talks and observations: WES/WGS, kissing snails, Poo bacteria sequencing
Wednesday, February 20, 2013
September (2)
Got fetal DNA on the brain?
Friday, September 28, 2012
Memes about 'junk DNA' miss the mark on paradigm shifting science
Friday, September 7, 2012
August (1)
So, you've dropped a cryovial or lost a sample box in your liquid nitrogen container...now what?
Thursday, August 16, 2012
July (1)February (1)
A peril of "Open" science: Premature reporting on the death of #ArsenicLife
Thursday, February 2, 2012
2011 (20)Got fetal DNA on the brain?
Friday, September 28, 2012
Memes about 'junk DNA' miss the mark on paradigm shifting science
Friday, September 7, 2012
So, you've dropped a cryovial or lost a sample box in your liquid nitrogen container...now what?
Thursday, August 16, 2012
A peril of "Open" science: Premature reporting on the death of #ArsenicLife
Thursday, February 2, 2012
October (7)
Antineoplastons? You gotta be kidding me!
Thursday, October 27, 2011
YouTube: Just a (PhD) Dream
Thursday, October 27, 2011
Slides - From the Bench to the Blogosphere: Why every lab should be writing a science blog
Wednesday, October 19, 2011
Fact Checking AARP: Why soundbytes about shrimp on treadmills and pickle technology are misleading
Monday, October 17, 2011
MHV68: Mouse herpes, not mouth herpes, but just as important
Monday, October 17, 2011
@DonorsChoose update: Pictures of the materials we bought being used!!
Friday, October 14, 2011
Is this supposed to be a feature, @NPGnews ?
Tuesday, October 4, 2011
August (3)
A dose of batshit crazy: Bachmann would drill in the everglades if elected president
Monday, August 29, 2011
A true day in lab
Wednesday, August 10, 2011
A day in the lab...
Monday, August 8, 2011
July (1)June (1)May (1)April (2)
University of Iowa holds Science Writing Symposium
Tuesday, April 26, 2011
Sonication success??
Monday, April 18, 2011
March (3)
Circle of life
Thursday, March 17, 2011
Curing a plague: Cryptocaryon irritans
Wednesday, March 9, 2011
Video: First new fish in 6 months!!
Wednesday, March 2, 2011
February (1)January (1)
2010 (13)Antineoplastons? You gotta be kidding me!
Thursday, October 27, 2011
YouTube: Just a (PhD) Dream
Thursday, October 27, 2011
Slides - From the Bench to the Blogosphere: Why every lab should be writing a science blog
Wednesday, October 19, 2011
Fact Checking AARP: Why soundbytes about shrimp on treadmills and pickle technology are misleading
Monday, October 17, 2011
MHV68: Mouse herpes, not mouth herpes, but just as important
Monday, October 17, 2011
@DonorsChoose update: Pictures of the materials we bought being used!!
Friday, October 14, 2011
Is this supposed to be a feature, @NPGnews ?
Tuesday, October 4, 2011
A dose of batshit crazy: Bachmann would drill in the everglades if elected president
Monday, August 29, 2011
A true day in lab
Wednesday, August 10, 2011
A day in the lab...
Monday, August 8, 2011
University of Iowa holds Science Writing Symposium
Tuesday, April 26, 2011
Sonication success??
Monday, April 18, 2011
Circle of life
Thursday, March 17, 2011
Curing a plague: Cryptocaryon irritans
Wednesday, March 9, 2011
Video: First new fish in 6 months!!
Wednesday, March 2, 2011
December (3)
The first step is the most important
Thursday, December 30, 2010
Have we really found a stem cell cure for HIV?
Wednesday, December 15, 2010
This paper saved my graduate career
Tuesday, December 14, 2010
November (3)
Valium or Sex: How do you like your science promotion
Tuesday, November 23, 2010
A wedding pic.
Tuesday, November 16, 2010
To rule by terror
Tuesday, November 9, 2010
October (2)
Summary Feed: What I would be doing if I wasn't doing science
Wednesday, October 6, 2010
"You have more Hobbies than anyone I know"
Tuesday, October 5, 2010
September (5)
Hiccupping Hubris
Wednesday, September 22, 2010
A death in the family :(
Monday, September 20, 2010
The new lab fish!
Friday, September 10, 2010
What I wish I knew...Before applying to graduate school
Tuesday, September 7, 2010
Stopping viruses by targeting human proteins
Tuesday, September 7, 2010
The first step is the most important
Thursday, December 30, 2010
Have we really found a stem cell cure for HIV?
Wednesday, December 15, 2010
This paper saved my graduate career
Tuesday, December 14, 2010
Valium or Sex: How do you like your science promotion
Tuesday, November 23, 2010
A wedding pic.
Tuesday, November 16, 2010
To rule by terror
Tuesday, November 9, 2010
Summary Feed: What I would be doing if I wasn't doing science
Wednesday, October 6, 2010
"You have more Hobbies than anyone I know"
Tuesday, October 5, 2010
Hiccupping Hubris
Wednesday, September 22, 2010
A death in the family :(
Monday, September 20, 2010
The new lab fish!
Friday, September 10, 2010
What I wish I knew...Before applying to graduate school
Tuesday, September 7, 2010
Stopping viruses by targeting human proteins
Tuesday, September 7, 2010
 |
 |
Blogger Profile
Brian Krueger, PhD
Columbia University Medical Center
New York NY USA
Brian Krueger is the owner, creator and coder of LabSpaces by night and Next Generation Sequencer by day. He is currently the Director of Genomic Analysis and Technical Operations for the Institute for Genomic Medicine at Columbia University Medical Center. In his blog you will find articles about technology, molecular biology, and editorial comments on the current state of science on the internet.
My posts are presented as opinion and commentary and do not represent the views of LabSpaces Productions, LLC, my employer, or my educational institution.
Please wait while my tweets load 
 |
 |
Post Tags
youtube sequencing genetics technology conference wedding pictures not science contest science promotion outreach internet cheerleaders rock stars lab science tips and tricks chip-seq science politics herpesviruses
 |
 |
Around the Network
Author: Brian Krueger, PhD | Comments: 9
Author: Brian Krueger, PhD | Comments: 0
Author: Brian Krueger, PhD | Comments: 2
Author: Brian Krueger, PhD | Comments: 2
 |
 |
Blogroll
Drugmonkey (Scientopia)
How AAAS and Science magazine really feel about sexual harassment cases in science
Mar 10, 2016, 1:37pm
Mar 08, 2016, 11:30am
Jul 14, 2011, 8:33pm
Views: 7750 | Comments: 0
Almost a year and a half ago, NASA ignited a media firestorm after it announced the discovery of a new organism with alien implications. The whole fiasco began when a scientist found a new bacteria in Mono Lake that could grow in the presence of high concentrations of toxic compounds. These types of bacteria are not uncommon on earth. Life seems to find a way to thrive at all extremes and a salty lake in California is no exception to this rule. Researchers have discovered a diversity of life in hot springs, at undersea volcanic vents, and on the cold arctic sea floor. The discovery of this new bacteria; however, was remarkable because the researchers believed that it could use arsenic in the place of phosphate. To the general public, this may sound trivial, but many of the biochemical reactions that provide life require phosphates. The reason why arsenic is so toxic to humans is that it injects itself into all of the processes that use phosphate and prevents those processes from working properly. For example, the molecular backbone that keeps our DNA together is composed of phosphate; the energetic molecules that are produced by the power factories in our cells are composed of phosphate; the specific addition of phosphate to some proteins turns them on or off. Phosphate and its derivatives are essential for life, so to find a bacteria that could function without phosphate and use arsenic in its place was an amazing discovery.
. . . More
. . . More
Views: 8434 | Comments: 0
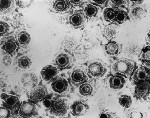
In the current political climate it has become clear that science is a major target of Republican directed budget cuts. However, the soundbytes of politics do not represent the importance of science in our lives. Because of this, I think it's extremely important that we explain why some of our model systems are so important for understanding how viruses and ultimately human disease work.
In the lab that I run, we currently work on mutating two different herpesviruses. One of these is Kaposi's Sarcoma Herpesvirus (KSHV) and the other is Murid Herpesvirus 68 (MHV68). Both of these viruses are gammaherpesviruses. In humans, KSHV only really ever becomes a problem in individuals who have a compromised immune system such as those infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). KSHV is an interesting virus because its default program is latency, meaning that once it gets into your cells, it turns itself off and waits for conditions which allow it to grow and take over. This is akin to a bear hibernating in the winter. We do not understand how or w . . . More
In the lab that I run, we currently work on mutating two different herpesviruses. One of these is Kaposi's Sarcoma Herpesvirus (KSHV) and the other is Murid Herpesvirus 68 (MHV68). Both of these viruses are gammaherpesviruses. In humans, KSHV only really ever becomes a problem in individuals who have a compromised immune system such as those infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). KSHV is an interesting virus because its default program is latency, meaning that once it gets into your cells, it turns itself off and waits for conditions which allow it to grow and take over. This is akin to a bear hibernating in the winter. We do not understand how or w . . . More
Views: 19325 | Comments: 136
Last by Isabel on Nov 26, 2010, 3:02pm
Last by Isabel on Nov 26, 2010, 3:02pm

With the launch of this year’s “Rock Stars of Science” campaign, there’s been a lot of talk about how to best promote science. I’m no marketing guru, but I am a scientist. This latest campaign is better than last years', only because it’s more diverse, but I think it really misses the boat. Is the public really going to be inspired by a couple of pictures in GQ of scientists looking uncomfortable and over dressed in the presence of Rock Stars? The most appalling aspect of this campaign is that there is no highlight of the researchers or their science. There truly are some science all stars in this group, many of which are well spoken.
However, the Rock Stars of science pages in GQ only list the scientist’s name and title, while the “Rock stars” get a one or two sentence summary of how awesome they are for standing in on these pictures. What’s the real focus of this campaign? To promote Bret Michaels’ latest reality TV dreck? If a reader wants to actually understand why these scientists were chosen and what they’re doing to cure disease, they have to visit the website. I find it hard to believ . . . More
However, the Rock Stars of science pages in GQ only list the scientist’s name and title, while the “Rock stars” get a one or two sentence summary of how awesome they are for standing in on these pictures. What’s the real focus of this campaign? To promote Bret Michaels’ latest reality TV dreck? If a reader wants to actually understand why these scientists were chosen and what they’re doing to cure disease, they have to visit the website. I find it hard to believ . . . More
 |
 |
Friends





Jaeson, that's not true at most places. Top tier, sure, but 1100+ should get you past the first filter of most PhD programs in the sciences. . . .Read More
All I can say is that GRE's really do matter at the University of California....I had amazing grades, as well as a Master's degree with stellar grades, government scholarships, publication, confere. . .Read More
Hi Brian, I am certainly interested in both continuity and accuracy of PacBio sequencing. However, I no longer fear the 15% error rate like I first did, because we have more-or-less worked . . .Read More
Great stuff Jeremy! You bring up good points about gaps and bioinformatics. Despite the advances in technology, there is a lot of extra work that goes into assembling a de novo genome on the ba. . .Read More
Brian,I don't know why shatz doesn't appear to be concerned about the accuracy of Pacbio for plant applications. You would have to ask him. We operate in different spaces- shatz is concerned a. . .Read More